veScale Pipeline Parallel (PP)
TLDR
What is PP?
Pipeline Parallel (PP) partitions layers of a model across multiple devices to form a pipelined execution of the training.
PP takes as input a list of microbatches of data per iteration and performs pipelined training execution (forward, backward, and optimizer update) on each microbatch, while overlaps communication with computation on each device.
Why veScale PP?
Existing PP systems suffer multiple drawbacks as below, which prevent productization within a company:
-
Complex API: assuming that model developers are also systems experts in
PP -
Hacking model code: requiring manually rewrite the model code to run
PP -
Lacking single device abstraction: requiring manually rewrite the training script to be
PPdevice-specific -
Lacking options of pipeline construction: relying on a single option of graph tracing, or perfect graph tracing, or solely manual construction of the pipeline.
-
Lacking customizability of pipeline schedule: deeply coupling the entire runtime (e.g., compute, communication) with a specific
PPschedule (e.g.,1F1B) -
Lacking diverse model support: supporting only sequential model architecture without branching, or supporting only pipeline stages having single input or single output without multiple input/output.
What is veScale PP?
veScale PP offers a new PP framework that is both Easy-to-Use and Easy-to-Customize, thus it is used internally in our production.
Especially, veScale PP provides:
-
Easy API: hiding the complexity of
PPsystems and runtimes from model developers -
Zero model code change: keeping the original torch model code as it is for transparent pipelined models
-
Single device abstraction: keeping the single device training script as it is for transparent pipelined training on multiple devices
-
Multiple options of pipeline construction: user can flexibly choose modes:
-
GRAPH_EAGERmode automatically traces and parses the model into a graph, splits the graph into pipeline stages, and constructs each stage for pipeline execution- graph tracer can also be choices or users
-
MANUAL_EAGERmode manually constructs each pipeline stage for pipeline execution, without graph tracing, parsing, and splitting.
-
-
Customizable pipeline schedule: empowering users to define their custom pipeline schedules, beyond our built-in schedule as below:
-
1F1B -
Interleaved 1F1B -
Zero Bubble
-
-
Support diverse models: support comprehensive model archictures for non-sequential models, multiple-input-multiple-output stages, and etc.
Why is veScale PP a better option than its counterparts?
-
Compared with Megatron-LM's PP,
veScale PPoffers not only a better Ease-of-Use experience in all aspects (easy API, zero model code, single device abstraction, options of pipeline construction) but also a plus of Customizability allowing users to conveniently customize new pipeline schedules. -
Compared with DeepSpeed,
veScale PPrequires no modification of model code. It further supports multi-stage scheduling for non-sequential multimodal architecture and multi-input settings instead of being constrained bynn.Sequential's syntax. -
Compared with the pre-release torchtitan,
veScale PPprovides: i) single device abstraction of training script, ii) wider options of graph tracer support, iii) wider model architecture support, and iv) guarantees bitwise accuracy alignment betweenPPand single device code.
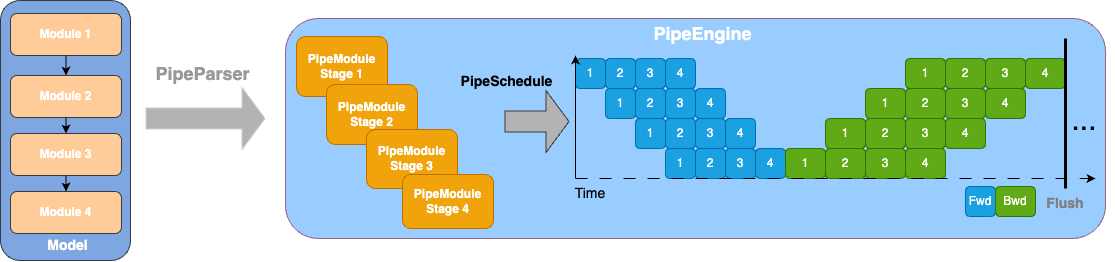
How does veScale PP work?
Spinning up a PP job typically requires three steps: i) trace and parse model graph, ii) construct pipeline stage, and iii) execute pipeline schedule. Each step is handled by PipeParser, PipeModule, and PipeEngine. Upon receiving the model definition, PipeParser (GRAPH_EAGER mode) breaks down the model code to the intermediate representation of low-level modules and operators up to the granularity of your choice. Under MANUAL_EAGER mode, users only need to assign stage modules and their communication relationships. PipeModule collects parameters and operators, and optimizer states belonging to the same stage, and resolves communication topology among devices. PipeEngine will schedule steps to execute training according to pipeline schedules.
How to use veScale PP?
-
Example of using
GRAPH_EAGERmode: -
Example of using
MANUAL_EAGERmode: Coming Soon. -
APIs can be found in
<repo>/vescale/pipe/pipe_stage.pyand<repo>/vescale/pipe/pipe.py -
More examples can be found in
<repo>/test/parallel/pipeline/api/test_simple_api.py

